Effluent Treatment Plants
Effluent Treatment Plant, Conventional
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) are used by companies in the pharmaceutical,textile &tanneries,leather and chemical industry to purify water and remove any toxic and non-toxic materials or chemicals from it. These plants are used by all companies for environment protection. An ETP is a plant where the treatment of industrial effluents and waste waters is done. The ETP plants are used widely in industrial sector, for example, pharmaceutical industry, to remove the effluents from the bulk drugs. During the manufacturing process of drugs, varied effluents and contaminants are produced. The effluent treatment plants are used in the removal of high amount of organics, debris, dirt, grit, pollution, toxic, non-toxic materials, polymers etc. The ETP plants use evaporation and drying methods, and other auxiliary techniques such as centrifuging, filtration, incineration for chemical processing and effluent treatment. The ETPs can be established in the industrial sectors like Pharmaceuticals,Textile ,Chemicals, Oil refinery and Leather industry and tanneries.
Treatment Methods
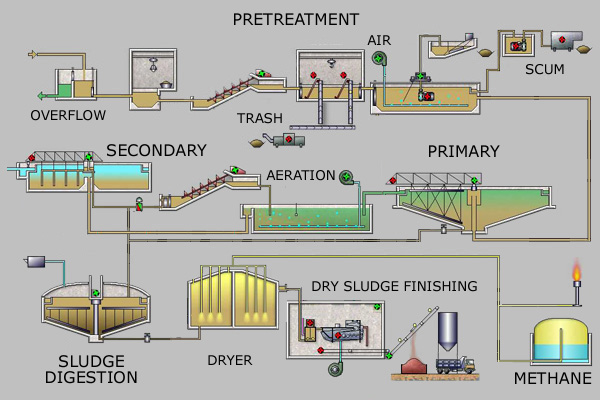
1. Pre Treatment
A. Coarse Screen Chamber : The Effluent is screened for removal of all Debris which are 10 mm and above sizes inadvertently flows along with the effluent before Equalization Tank. B. Grit Chamber cum Parshall Flume : The Grits (if any) are allowed to be accumulated in the Grit chamber / channel and passes through the Parshall flume to measure the Flow
2. Primary Treatment:
C. Equalization Tank: The Effluent (waste water) from all the industries is collected in this Tank which is provided with Coarse Bubble Aeration system to equalize for the concentration such as BOD, COD & TSS before taken for further treatment units. D. Flash Mixing & Flocculation:Lime, Alum is Flash Mixed with the Equalized waste water and then flocculated with Polyelectrolyte before taken into the Primary Clarifier. The Coagulants help in making the suspended solids to agglomerate into bigger floc particle which settles faster.
E. Primary Clarifier:Primary Clarification removes by means of settling excess suspended solids & sludge generated after degradation of the impurities. The Sludge is scrapped with the help of Scrapper Mechanism and withdrawn with the help of Primary Sludge Pump in to the Sludge Collection Tank. The supernatant is allowed to overflow to the Aeration tank for further biodegradation under aerobic condition.
3. Secondary Treatment:
The Effluent after primary treatment is subjected to secondary treatment. The major goal of this treatment is to remove soluble Pollutants by oxidation & settling. This involves bringing the active microbes in contact with waste water which consume the Organic matters as food. These organisms; in presence of Oxygen ( O2 ), convert the biodegradable organics into Carbon Di Oxide ( CO2 ) , Water, Nitrogen & more cell material and other inert products. During this process Microbes use some Inorganic & Metallic compounds for their growth There are various processes of Biological Treatments. i. Activated Sludge Process ii. Activated Sludge Process with SAFF / Bio-deck. iii. Trickling Filter / Bio-Tower. iv. Rotating Biological Contactor (RBC). F. Activated sludge Process (Aeration Tank / Bio-Reactor):Here the non-settleable& bio-degradable organics present in the Effluent (waste water) are treated bio-chemically. This process is utilized to convert non-settleable, bio- degradable matters dissolved and colloidal solids into settleable sludge. System is designed to maintain high MLSS and Low F/M ratio. The aeration in the Aeration Tank / Bio-Reactor is carried through Fine bubble Membrane diffused aeration system.
G. Secondary Clarifier: The Effluent (waste water) along with Bio-Mass from Aeration Tank /Bio-Reactor overflows by gravity to Secondary Clarifier. Active biomass get settle at the bottom of tank. Part of the active biomass is recycled back to Aeration Tank / Bio-reactor with the help of RAS (return Activated Sludge) Pump to maintain required population of bacteria (MLSS) and excess biomass is sent to sludge collection Sump. The Biological Sludge is scrapped with the help of Scrapper Mechanism and is pumped to the Sludge Tank.
4. Tertiary Treatment:
The water from the secondary treatment is then collected in Filter Feed Tank and it is once again pumped through Pressure Sand Filter (PSF) & Activated Carbon Filter (ACF). The Pressure Sand Filter employed with quartz sand media & Down-flow system during filtration. It is designed to reduce the suspended solids present in the supernatant in micronic size. In a cycle of 12 hrs., the PSF is back washed to avoid clogging & to have quality filtration. 7 The Activated Carbon Filter Filled with Activated Carbon & Down-flow system during filtration. It is designed to reduce the Soluble Organic Compound and Traces of Heavy metals if any present in the water. In a cycle of 12 hrs. , the ACF is back washed to avoid clogging & to have quality filtration. I. Chlorination: The waste water from the Secondary clarifier is passed through the Chlorine contact through pipeline / zone Baffled type before allowed for Filtration. Liquid chlorination (NaOCl) is adopted from safety point. Prior to pumping into the Filters Chlorination is adopted to kill the bacteria to avoid the growth of bacteria inside the Filters as well as further contamination in the downstream. Sludge: Sludge collected from the Primary Clarifier & Secondary Clarifier in the Sludge Tank is further pumped through the Filter Press to dewater and form the sludge cake. The sludge cake is further put into the Sludge Drying Bed to reduce the weight. The dewatered
